2. Control of nitriding layer structure
The microstructure of the surface of the nitrided layer directly affects the brittleness of the tooth surface and the mechanical properties such as the fatigue strength of the gear. One of the main advantages of the ion nitriding process is that different phase components can be obtained by controlling the ratio of nitrogen to hydrogen in the furnace atmosphere. According to a literature, under the experimental conditions, when ion nitriding is carried out in a medium atmosphere with w Ni = 8% to 12%, a compound layer structure of γ' single phase can be obtained, and when the nitrogen content is 5%, it can be obtained. Pure diffusion layer structure without compound layer. For the 42CrMo and 40CrNiMo materials with 0.4 C of w C ≈, a certain amount of ε phase is formed due to the high carbon content, and a single phase structure of complete γ′ is not easily obtained.
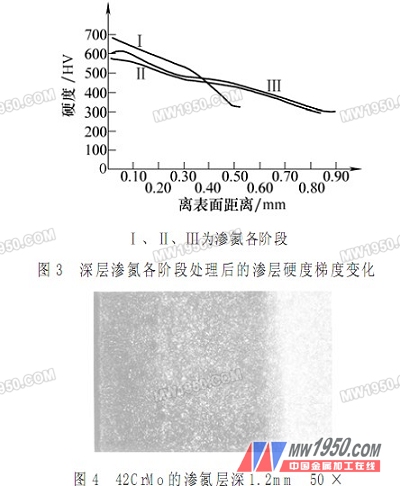
3. Deep nitriding layer acquisition
The thickness of the conventional nitrided layer is generally below 0.6 mm, and deep nitriding of 0.8 to 1.2 mm is carried out, which tends to greatly prolong the treatment time. In order to make the deep nitriding process easy to be applied in industry, it is necessary to ensure that the process cycle is not too long, and an effective measure is to increase the nitriding temperature, but this is constrained by the hardening effect of the medium hard matrix and the good nitriding layer. The three-stage process is processed.
The first stage of strong infiltration: the purpose of this stage of treatment is to make the outer surface of the gear rich in higher nitrogen concentration in the shortest possible time to obtain a larger gradient of nitrogen concentration for later diffusion at higher temperatures. A higher barrier increases the diffusion rate of nitrogen. The temperature is generally 520 ~ 530 ° C, time 12 ~ 15h, the surface nitrogen concentration can be saturated, the time is extended, the significance is not significant.
The second stage of expansion: on the basis of the first stage, it is necessary to strengthen the diffusion of nitrogen atoms inside the steel, it is necessary to appropriately increase the treatment temperature to increase the diffusion coefficient of nitrogen, and obtain a hard layer with a deeper and gentle hardness gradient. The increase of temperature can not affect the strength of the medium-hard matrix, but also take into account the side effects of temperature increase on the gear deformation, generally take 570 ~ 580 ° C, the expansion time can be about 40h.
The third stage of percolation: after the expansion, the microhardness decreased in different extents within the depth of 0.3mm. This is because the diffusion of nitrogen at a certain depth is reduced by prolonged diffusion at a higher temperature, and the nitride has a certain degree of aggregation and the coherent relationship with the parent phase is destroyed, and the elastic distortion stress field acts. Weakened, the obstacle to the movement of dislocations is reduced. For this reason, the same process as the first stage of strong infiltration is used to make the seepage to improve the hardening effect of the layer.
The microhardness gradient after completion of each stage in the three-stage nitriding process is shown in Figure 3. The depth of the layer can reach 0.8-1.2mm (see Figure 4), the surface hardness can reach 550-570HV, and the surface layer of the compound layer with γ' phase as the main or single phase can be obtained.
Previous Next
Magnetic Ring,Strong Magnetic Ring,Ndfeb Magentic Ring
Sunny Fore Magnet Company Limited , http://www.jmmagnet.com